Diamond forms during low pressure serpentinisation of oceanic lithosphere
Affiliations | Corresponding Author | Cite as | Funding information- Share this article




-
Article views:182Cumulative count of HTML views and PDF downloads.
- Download Citation
- Rights & Permissions
top
Abstract
Figures
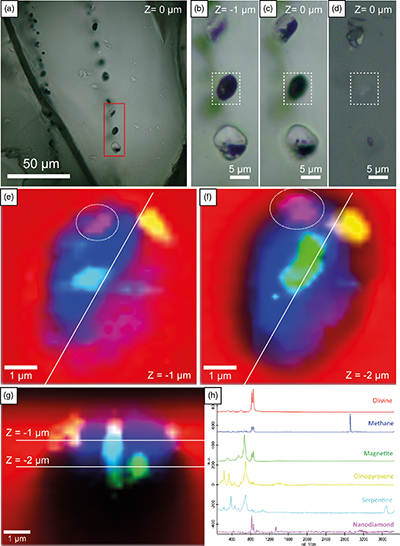 Figure 1 (a) Transmitted light photomicrograph (TLP) of olivine hosting a trail of secondary fluid inclusions. The red area defines the zoom in (b-d). (b, c) TLP of fluid inclusions below the surface of olivine with focus at Z (depth) = −1 and 0 μm respectively. (d) Reflected light photomicrograph of (c), showing that the central inclusion is completely below the surface. White rectangles mark the area of (e-g). (e) Fluid inclusion confocal Raman map at Z = −1 μm; different colours represent different phases. (f) Confocal Raman map for the same inclusion at Z = −2 μm. (g) Z-stack of (e, f) showing the inclusion profile. (h) Raman spectra of the identified phases (colour coded). Mapping conditions: 6 × 6 μm, 30 × 30 spectra, Tint = 2 s, 2 mW, 100× objective. | 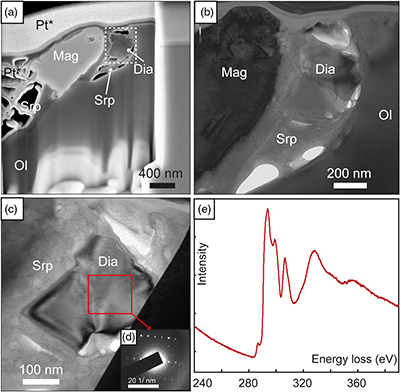 Figure 2 (a) Field emission scanning electron microscope image of olivine-hosted inclusion thinned by focused ion beam. (b,c) TEM image of the diamond and the surrounding serpentine and magnetite; the red square shows the selected area electron diffraction (SAED). (d) SAED pattern confirming the diamond structure of the crystal (the nearly horizontal rows of reflections have indices 111 with d spacing of 2 Å). (e) Electron energy loss near-edge structure of the C K-edge for the diamond showing a major peak due to its sp3 bonding. Abbreviations: Dia-Diamond, Mag-magnetite, Ol-olivine, Srp-serpentine, Pt*-platinum deposited during sample preparation. | 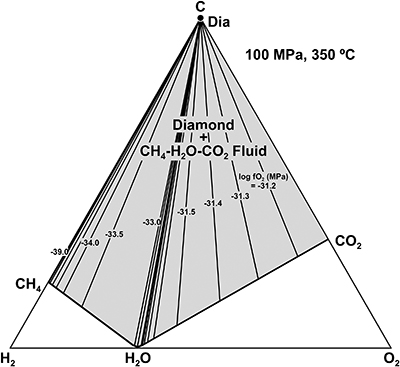 Figure 3 Phase relations in the C-O-H system (see methods in SI for details) with indication of fO2 isopleths (black solid lines, log-units) for the diamond-(Dia) saturated portion (log(aC) = 0) of the system at 100 MPa, 350 °C. |
| Figure 1 | Figure 2 | Figure 3 |
top
Introduction
The discovery of nano- to micrometre scale grains of diamond separated from ophiolitic rocks has recently attracted the attention of geoscientists due to its potential evidence for lithosphere recycling down to, or below, the mantle Transition Zone (e.g., Yang et al., 2007
Yang, J.S., Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Bai, W.J., Fang, Q.S., Robinson, P.T., Zhang, J., Green, H.W. (2007) Diamond- and coesite-bearing chromitites from the Luobusa ophiolite, Tibet. Geology 35, 875–878.
, 2015Yang, J., Meng, F., Xu, X., Robinson, P.T., Dilek, Y., Makeyev, A.B., Wirth, R., Wiedenbeck, M., Cliff, J. (2015) Diamonds, native elements and metal alloys from chromitites of the Ray-Iz ophiolite of the Polar Urals. Gondwana Research 27, 459–485.
; Griffin et al., 2016Griffin, W.L., Afonso, J.C., Belousova, E.A., Gain, S.E., Gong, X.H., González-Jiménez, J.M., Howell, D., Huang, J.X., McGowan, N., Pearson, N.J., Satsuawa, T., Shi, R., Williams, P., Xiong, Q., Yang, J.S., Zhang, M., O’Reilly, S.Y. (2016) Mantle Recycling: Transition Zone Metamorphism of Tibetan Ophiolitic Peridotites and its Tectonic Implications. Journal of Petrology 57, 655–684.
). The earlier reports of diamond in nominally low pressure ophiolitic rocks date back to the early 1990s, when diamond was found in heavy mineral concentrates obtained from Tibetan ophiolites (Bai et al., 1993Bai, W.J., Zhou, M.F., Robinson, P.T. (1993) Possibly diamond-bearing mantle peridotites and podiform chromitites in the Luobusa and Donqiao ophiolites, Tibet. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 30, 1650–1659.
). These were initially considered to be due to contamination during sample preparation. The debate, however, rejuvenated after findings of other UHP minerals such as coesite together with super-reduced phases in many chromitites and associated peridotites of ophiolites worldwide (e.g., Griffin et al., 2016Griffin, W.L., Afonso, J.C., Belousova, E.A., Gain, S.E., Gong, X.H., González-Jiménez, J.M., Howell, D., Huang, J.X., McGowan, N., Pearson, N.J., Satsuawa, T., Shi, R., Williams, P., Xiong, Q., Yang, J.S., Zhang, M., O’Reilly, S.Y. (2016) Mantle Recycling: Transition Zone Metamorphism of Tibetan Ophiolitic Peridotites and its Tectonic Implications. Journal of Petrology 57, 655–684.
). Far-reaching geodynamic models have been proposed based on the assumption that diamond growth took place at UHP conditions in these rocks (e.g., Barron et al., 1996Barron, L.M., Lishmund, S.R., Oakes, G.M., Barron, B.J., Sutherland, F.L. (1996) Subduction model for the origin of some diamonds in the Phanerozoic of eastern New South Wales. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 43, 257–267.
; Xiong et al., 2019Xiong, F., Liu, Z., Kapsiotis, A., Yang, J., Lenaz, D., Robinson, P.T. (2019) Petrogenesis of lherzolites from the Purang ophiolite, Yarlung-Zangbo suture zone, Tibet: origin and significance of ultra-high pressure and other ‘unusual’ minerals in the Neo-Tethyan lithospheric mantle. International Geology Review 61, 2184–2210.
and references therein). Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a)Farré-de-Pablo, J., Proenza, J.A., González-Jiménez, J.M., Garcia-Casco, A., Colás, V., Roqué-Rosell, J., Camprubí, A., Sánchez-Navas, A. (2019a) A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, 75–78.
provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015Simakov, S.K., Kouchi, A., Mel’nik, N.N., Scribano, V., Kimura, Y., Hama, T., Suzuki, N., Saito, H., Yoshizawa, T. (2015) Nanodiamond finding in the hyblean shallow mantle xenoliths. Scientific Reports 5, 10765, doi: 10.1038/srep10765.
, 2020Simakov, S.K., Scribano, V., Mel’Nik, N.N., Barone, G. (2020) Sicilian serpentinite xenoliths containing abiotic organics with nanodiamond clusters as key model for prebiotic processes. Geoscience Frontiers (in press), doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.008.
), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008Simakov, S.K., Dubinchuk, V.T., Novikov, M.P., Drozdova, I.A. (2008) Formation of diamond and diamond-type phases from the carbon-bearing fluid at PT parameters corresponding to processes in the Earth’s crust. Doklady Earth Sciences 421, 835–837.
) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013Manuella, F.C. (2013) Can nanodiamonds grow in serpentinite-hosted hydrothermal systems? A theoretical modelling study. Mineralogical Magazine 77, 3163–3174.
; Simakov, 2018Simakov, S.K. (2018) Nano- and micron-sized diamond genesis in nature: An overview. Geoscience Frontiers 9, 1849–1858.
) work on low pressure growth of diamond. However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019bFarré-de-Pablo, J., Proenza, J.A., González-Jiménez, J.M., Garcia-Casco, A., Colás, V., Roqué-Rosell, J., Camprubí, A., Sánchez-Navas, A. (2019b) A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites: REPLY. Geology 47, e477–e478, doi: 10.1130/G46602Y.1.
; Massonne, 2019Massonne, H.J. (2019) Comment: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e476, doi: 10.1130/G46459C.1.
; Yang et al., 2019Yang, J., Lian, D., Robinson, P.T., Qiu, T., Xiong, F., Wu, W. (2019) Comment to: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e475, doi: 10.1130/G46446C.1.
). In this regard, Litasov et al. (2019aLitasov, K.D., Kagi, H., Voropaev, S.A., Hirata, T., Ohfuji, H., Ishibashi, H., Makino, Y., Bekker, T.B., Sevastyanov, V.S., Afanasiev, V.P., Pokhilenko, N.P. (2019a) Comparison of enigmatic diamonds from the Tolbachik arc volcano (Kamchatka)and Tibetan ophiolites: Assessing the role of contamination by synthetic materials. Gondwana Research 75, 16–27.
,bLitasov, K.D., Kagi, H., Bekker, T.B., Hirata, T., Makino, Y. (2019b) Cuboctahedral type Ib diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites and peridotites: the evidence for anthropogenic contamination. High Pressure Research 39, 480–488.
) have recently claimed that most diamonds, if not all, from ophiolitic rocks are not natural but instead have a synthetic origin, and emphasised the need to identify diamond below the polished surface of the host mineral. In this study we report for the first time in situ diamond grains hosted below the polished surface of magmatic olivine from a low pressure gabbro sill of the upper mantle section of the Moa-Baracoa Ophiolitic Massif, eastern Cuba (Supplementary Information; Figs. S-1–S-4, Table S-1), where super-reduced phases formed during serpentinisation have been previously reported (Pujol-Solà et al., 2018Pujol-Solà, N., Proenza, J., Garcia-Casco, A., González-Jiménez, J., Andreazini, A., Melgarejo, J., Gervilla, F. (2018) An Alternative Scenario on the Origin of Ultra-High Pressure (UHP) and Super-Reduced (SuR) Minerals in Ophiolitic Chromitites: A Case Study from the Mercedita Deposit (Eastern Cuba). Minerals 8, 433, doi: 10.3390/min8100433.
). Diamond grains, which are also present in olivine of associated chromitite, occur in secondary inclusions within olivine. Our observations provide conclusive evidence for the natural formation of metastable diamond at low P (<200 MPa) and low T (<350 °C) during serpentinisation of oceanic mafic and ultramafic rocks, and allow a word of caution on the development of generalised geodynamic models of mantle convection and lithosphere recycling into the deep mantle based on diamond and super-reduced phases alone.top
Results
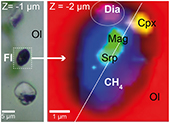
We have studied approximately 150 inclusions (96 below the polished surface) in olivine from 5 gabbro thin sections and 16 inclusions (8 below the surface) hosted in olivine in chromitite (representative inclusions in Table S-2). The inclusions align along trails that extend across adjacent mineral grains and delineate healed fractures (Fig. 1a–d). The distribution of these trails is heterogeneous, with some olivine grains showing a high density of trails cross-cutting each other. Inclusions are typically spheroid, with sizes ranging between <1 μm and 14 μm in diameter (Figs. 1a–d, S-2).
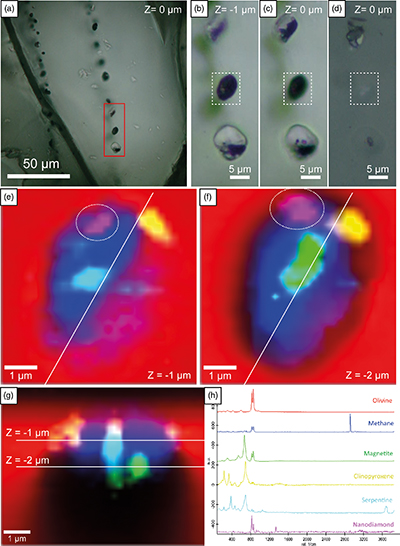
Figure 1 (a) Transmitted light photomicrograph (TLP) of olivine hosting a trail of secondary fluid inclusions. The red area defines the zoom in (b-d). (b, c) TLP of fluid inclusions below the surface of olivine with focus at Z (depth) = −1 and 0 μm respectively. (d) Reflected light photomicrograph of (c), showing that the central inclusion is completely below the surface. White rectangles mark the area of (e-g). (e) Fluid inclusion confocal Raman map at Z = −1 μm; different colours represent different phases. (f) Confocal Raman map for the same inclusion at Z = −2 μm. (g) Z-stack of (e, f) showing the inclusion profile. (h) Raman spectra of the identified phases (colour coded). Mapping conditions: 6 × 6 μm, 30 × 30 spectra, Tint = 2 s, 2 mW, 100× objective.
Diamond grains were identified with the characteristic Raman peak at 1330 cm−1 with a slight downshift from the typical band to 1326 cm−1 (n = 17; Table S-2) lining the walls of inclusions (Fig. 1e–f). These very small (200–300 nm) diamond grains were better characterised by confocal Raman maps at different depths (Fig. 1e–h). Nanodiamond is usually associated with methane, serpentine (lizardite, polygonal serpentine, chrysotile), and magnetite (Fig. 1h). Daughter minerals include diopside, chlorite, graphite-like amorphous C, and calcite (Table S-2, Fig. S-5). Brucite was not identified in any of the studied inclusions, similar to other locations (e.g., Sachan et al., 2007
Sachan, H.K., Mukherjee, B.K., Bodnar, R.J. (2007) Preservation of methane generated during serpentinization of upper mantle rocks: Evidence from fluid inclusions in the Nidar ophiolite, Indus Suture Zone, Ladakh (India). Earth and Planetary Science Letters 257, 47–59.
). However, brucite is a widespread product in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions in ophiolitic samples (e.g., Klein et al., 2019Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
; Grozeva et al., 2020Grozeva, N.G., Klein, F., Seewald, J.S., Sylva, S.P. (2020) Chemical and isotopic analyses of hydrocarbon-bearing fluid inclusions in olivine-rich rocks. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 378, 20180431.
).TEM observations of a thin foil extracted by focused ion beam (FIB) (Fig. 2a) reveal that nanodiamond is clearly surrounded by polygonal serpentine and associated with magnetite (Fig. 2b,c). The selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern of a grain a few hundreds of nanometres in size confirms its diamond structure (with a reciprocal distance of 5 nm−1 corresponding to the d111-spacing of 2 Å; Fig. 2d), while the corresponding electron energy loss spectrum (EELS) indicates that C-type is the diamond allotrope (sp3-hybridised C atoms; Fig. 2e). No polishing debris was observed in the studied inclusions, suggesting no contamination during ion milling of the thin foil except for sublimated Pt used to protect the area. The observed pore space in the inclusions (Figs. 2a, S-6) was likely filled by methane, as indicated by Raman spectroscopy measurements (Table S-2).
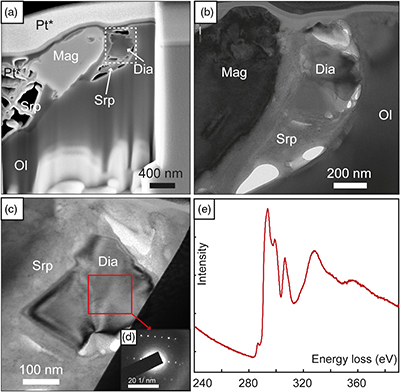
Figure 2 (a) Field emission scanning electron microscope image of olivine-hosted inclusion thinned by focused ion beam. (b,c) TEM image of the diamond and the surrounding serpentine and magnetite; the red square shows the selected area electron diffraction (SAED). (d) SAED pattern confirming the diamond structure of the crystal (the nearly horizontal rows of reflections have indices 111 with d spacing of 2 Å). (e) Electron energy loss near-edge structure of the C K-edge for the diamond showing a major peak due to its sp3 bonding. Abbreviations: Dia-Diamond, Mag-magnetite, Ol-olivine, Srp-serpentine, Pt*-platinum deposited during sample preparation.
Sub-surface fluid inclusions lack water and are dominated by methane (Table S-2), similarly to olivine-hosted fluid inclusions described by Klein et al. (2019)
Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
. In chromitite, diamond grains have been found in 5 sealed fracture-filling inclusions within interstitial magmatic olivine. One inclusion studied by TEM (Fig. S-7) revealed a <1 μm-sized diamond crystal coexisting with the super-reduced phase native Si. In addition, H2 was identified by Raman spectroscopy in another inclusion (Table S-2). Nevertheless, the phase assemblages are similar to those of the studied inclusions in olivine from the associated gabbro, with serpentine and magnetite (Fig. S-4, Table S-2).top
Natural Origin of the Studied Diamond
The natural vs. anthropogenic origin of ophiolitic diamond is a hotly debated topic. Whereas in other samples the natural origin of diamond has not been firmly proved (Massonne, 2019
Massonne, H.J. (2019) Comment: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e476, doi: 10.1130/G46459C.1.
), here we provide several lines of evidence for a natural origin. Our most significant evidence is that diamond is hosted within olivine well below the mineral’s polished surface (Fig. 1). Such an observation meets the basic requirements for in situ mineral grains, as suggested by Massonne (2019)Massonne, H.J. (2019) Comment: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e476, doi: 10.1130/G46459C.1.
. Additional evidence includes: (1) that diamond was found within CH4-bearing fluid inclusions forming linear arrays (healed fractures) in olivine and surrounded by serpentine (Figs. 1–2), and (2) lack of polishing debris and/or resin artificially incorporated (e.g., Dobrzhinetskaya et al., 2014Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Wirth, R., Green, H. (2014) Diamonds in Earth’s oldest zircons from Jack Hills conglomerate, Australia, are contamination. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 387, 212–218.
).top
Processes and Conditions for Diamond Formation
The olivine-hosted inclusion trails represent fluids trapped in healed fractures. Fluid infiltration in oceanic lithosphere is commonly associated with sporadic deformation events that trigger an increase of porosity by (micro-)fracturing during cooling below the brittle-ductile transition of olivine (Klein et al., 2019
Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
). In this scenario, fluid-rock interaction changes from a general open system during initial infiltration to closed system micro-reactors once the inclusions are sealed. At the initial trapping pressure and temperature and during subsequent cooling, the trapped aqueous fluids react with the olivine walls of the inclusion, triggering a number of reactions that ultimately result in growth of hydrated minerals and changes in fluid composition. Comprehensive thermodynamic models of these processes in ultramafic and oceanic rocks (McCollom and Bach, 2009McCollom, T.M., Bach, W. (2009) Thermodynamic constraints on hydrogen generation during serpentinization of ultramafic rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73, 856–875.
; Klein et al., 2019Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
) show that below ∼350 °C (at <200 MPa) in the stability field of serpentine + brucite “serpentinisation” of the walls of olivine hosting fluid inclusions consumes H2O in the fluid and generates H2 through precipitation of Fe3+-rich phases, particularly magnetite, so that consumption of inorganic carbon (CO2) and formation of abiotic CH4 takes place. In the 6 component system MgO-FeO-SiO2-C-O2-H2, the formation of phase assemblages made of serpentine, brucite, magnetite, diamond and CH4-fluid from an initial assemblage made of olivine and H2O-CO2 fluid can be described by a number of linearly independent reactions. Assuming 11 phase components (Fo, Fa, Mag, Mg-Srp, Mg-Brc, H2O, CO2, CH4, H2, SiO2(aq), C abbreviations after Whitney and Evans, 2010Whitney, D.L., Evans, B.W. (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. American Mineralogist 95, 185–187.
) appropriate for the low temperature stage of reaction progress, and excluding magnesite for simplicity, the dimension of the reaction space is 5. Among many, the following set of five linearly independent reactions obtained with the software CSpace (Torres-Roldán et al., 2000Torres-Roldán, R.L., Garcia-Casco, A., García-Sánchez, P.A. (2000) CSpace: An integrated workplace for the graphical and algebraic analysis of phase assemblages on 32-bit Wintel platforms. Computers and Geosciences 26, 779–793.
) describes the process (commonly used as coupled reactions during serpentinisation, e.g., Lamadrid et al., 2017Lamadrid, H.M., Rimstidt, J.D., Schwarzenbach, E.M., Klein, F., Ulrich, S., Dolocan, A., Bodnar, R.J. (2017) Effect of water activity on rates of serpentinization of olivine. Nature Communications 8, 1–9.
; Klein et al., 2019Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
):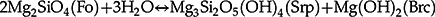

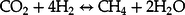



Connolly, J.A.D. (2009) The geodynamic equation of state: What and how. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 10, doi: 10.1029/2009GC002540.
). According to the low P conditions at which serpentinisation occurs, the stable C allotrope should be graphite. However, it has been demonstrated that nanodiamond can form at super-reducing conditions (e.g., Manuella, 2013Manuella, F.C. (2013) Can nanodiamonds grow in serpentinite-hosted hydrothermal systems? A theoretical modelling study. Mineralogical Magazine 77, 3163–3174.
; Simakov, 2018Simakov, S.K. (2018) Nano- and micron-sized diamond genesis in nature: An overview. Geoscience Frontiers 9, 1849–1858.
). Hence, in the above thermodynamic calculations, diamond has been used instead of graphite in order to simulate its metastable formation. The corresponding calculated log(fO2; MPa) is as low as −45.3, (ΔlogfO2[Iron-Magnetite] = −6.5; Frost, 1991Frost, B.R. (1991) Introduction to oxygen fugacity and its petrologic importance. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry 25, 1–9.
), consistent with thermodynamic calculations in the diamond-COH fluid system at 350 °C and 100 MPa (Fig. 3; cf. Schmidt et al., 2014Schmidt, M.W., Gao, C., Golubkova, A., Rohrbach, A., Connolly, J.A. (2014) Natural moissanite (SiC) – a low temperature mineral formed from highly fractionated ultra-reducing COH-fluids. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science 1, 27.
).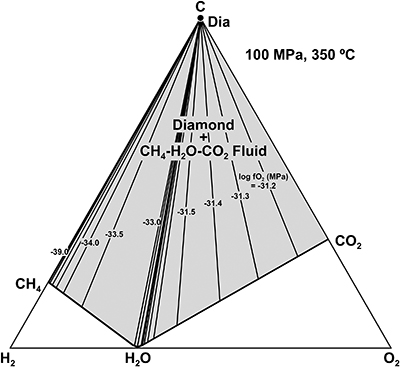
Figure 3 Phase relations in the C-O-H system (see methods in SI for details) with indication of fO2 isopleths (black solid lines, log-units) for the diamond-(Dia) saturated portion (log(aC) = 0) of the system at 100 MPa, 350 °C.
Admittedly, calculations in a more complex system, with additional components and minerals (e.g., CaO, clinopyroxene, talc, carbonates etc.) and constraints (e.g., dissolved silica in the fluid), and at other P-T conditions over which serpentinisation takes place, would yield a more intricate picture of the basic process outlined above and different absolute values of fO2 (e.g., Klein et al., 2019
Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
). However, a highly reduced environment (particularly at lower T, see e.g., Klein et al., 2019Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
) should develop if CH4 is to be the main fluid species in the inclusions, making possible the metastable formation of nanodiamond in low pressure, olivine-bearing oceanic rocks during low T infiltration of H2O-CO2 fluid mixtures.The undoubted natural origin of diamond hosted with serpentine, magnetite and CH4 in sealed fluid inclusions within magmatic olivine from a gabbro sill and associated chromitite should be related to the generalised release of CH4 during hydrothermal alteration (partial hydration) of shallow oceanic lithosphere (e.g., Klein et al., 2019
Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
). This finding implies that the formation of nanodiamond in altered olivine-bearing rocks can be a widespread process. The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019aFarré-de-Pablo, J., Proenza, J.A., González-Jiménez, J.M., Garcia-Casco, A., Colás, V., Roqué-Rosell, J., Camprubí, A., Sánchez-Navas, A. (2019a) A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, 75–78.
) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018Pujol-Solà, N., Proenza, J., Garcia-Casco, A., González-Jiménez, J., Andreazini, A., Melgarejo, J., Gervilla, F. (2018) An Alternative Scenario on the Origin of Ultra-High Pressure (UHP) and Super-Reduced (SuR) Minerals in Ophiolitic Chromitites: A Case Study from the Mercedita Deposit (Eastern Cuba). Minerals 8, 433, doi: 10.3390/min8100433.
) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007Yang, J.S., Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Bai, W.J., Fang, Q.S., Robinson, P.T., Zhang, J., Green, H.W. (2007) Diamond- and coesite-bearing chromitites from the Luobusa ophiolite, Tibet. Geology 35, 875–878.
, 2015Yang, J., Meng, F., Xu, X., Robinson, P.T., Dilek, Y., Makeyev, A.B., Wirth, R., Wiedenbeck, M., Cliff, J. (2015) Diamonds, native elements and metal alloys from chromitites of the Ray-Iz ophiolite of the Polar Urals. Gondwana Research 27, 459–485.
; Griffin et al., 2016Griffin, W.L., Afonso, J.C., Belousova, E.A., Gain, S.E., Gong, X.H., González-Jiménez, J.M., Howell, D., Huang, J.X., McGowan, N., Pearson, N.J., Satsuawa, T., Shi, R., Williams, P., Xiong, Q., Yang, J.S., Zhang, M., O’Reilly, S.Y. (2016) Mantle Recycling: Transition Zone Metamorphism of Tibetan Ophiolitic Peridotites and its Tectonic Implications. Journal of Petrology 57, 655–684.
). The small size of diamond (<1 μm) and its scarcity in the fluid inclusions are important handicaps in searching for “the needle in the haystack”, thus explaining its apparent absence in other case studies of altered oceanic rocks.top
Acknowledgements
We thank the editor H.R. Marschall and the reviewers F. Klein, I. Graham and C. Ballhaus for their constructive comments. This research was funded by Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) Funds, Spanish Projects CGL2015-65824, RTI2018-099157-A-I00, PID2019-105625RB-C21, and A.RNM.186.UGR18. Additional funding was provided by the Ramón y Cajal Fellowship RYC-2015-17596 to JMGJ, a FPU-PhD grant to NPS, the Mexican research programs CONACYT-Ciencia Básica (A1-S-14574) and UNAM-PAPIIT grant IA-101419, and received support for analyses at CIC from the University of Granada.
Editor: Horst R. Marschall
top
References
Bai, W.J., Zhou, M.F., Robinson, P.T. (1993) Possibly diamond-bearing mantle peridotites and podiform chromitites in the Luobusa and Donqiao ophiolites, Tibet. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 30, 1650–1659.
 Show in context
Show in context The earlier reports of diamond in nominally low pressure ophiolitic rocks date back to the early 1990s, when diamond was found in heavy mineral concentrates obtained from Tibetan ophiolites (Bai et al., 1993).
View in article
Barron, L.M., Lishmund, S.R., Oakes, G.M., Barron, B.J., Sutherland, F.L. (1996) Subduction model for the origin of some diamonds in the Phanerozoic of eastern New South Wales. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 43, 257–267.
 Show in context
Show in context Far-reaching geodynamic models have been proposed based on the assumption that diamond growth took place at UHP conditions in these rocks (e.g., Barron et al., 1996; Xiong et al., 2019 and references therein).
View in article
Connolly, J.A.D. (2009) The geodynamic equation of state: What and how. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems 10, doi: 10.1029/2009GC002540.
 Show in context
Show in context A bulk composition with an initial olivine:fluid ratio of 0.7∶0.3 produces an assemblage of 51.3 vol. % Ol (Fo = 0.76), 40.2 vol. % antigorite, 6.8 vol. % magnetite, 1.5 vol. % CH4 and 0.12 vol. % diamond at 100 MPa and 350 °C using the Perple_X software (Connolly, 2009).
View in article
Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Wirth, R., Green, H. (2014) Diamonds in Earth’s oldest zircons from Jack Hills conglomerate, Australia, are contamination. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 387, 212–218.
 Show in context
Show in context Additional evidence includes: (1) that diamond was found within CH4-bearing fluid inclusions forming linear arrays (healed fractures) in olivine and surrounded by serpentine (Figs. 1–2), and (2) lack of polishing debris and/or resin artificially incorporated (e.g., Dobrzhinetskaya et al., 2014).
View in article
Farré-de-Pablo, J., Proenza, J.A., González-Jiménez, J.M., Garcia-Casco, A., Colás, V., Roqué-Rosell, J., Camprubí, A., Sánchez-Navas, A. (2019a) A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, 75–78.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond.
View in article
The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019a) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
Farré-de-Pablo, J., Proenza, J.A., González-Jiménez, J.M., Garcia-Casco, A., Colás, V., Roqué-Rosell, J., Camprubí, A., Sánchez-Navas, A. (2019b) A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites: REPLY. Geology 47, e477–e478, doi: 10.1130/G46602Y.1.
 Show in context
Show in context However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
Frost, B.R. (1991) Introduction to oxygen fugacity and its petrologic importance. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry 25, 1–9.
 Show in context
Show in context The corresponding calculated log(fO2; MPa) is as low as −45.3, (ΔlogfO2[Iron-Magnetite] = −6.5; Frost, 1991), consistent with thermodynamic calculations in the diamond-COH fluid system at 350 °C and 100 MPa (Fig. 3; cf. Schmidt et al., 2014).
View in article
Griffin, W.L., Afonso, J.C., Belousova, E.A., Gain, S.E., Gong, X.H., González-Jiménez, J.M., Howell, D., Huang, J.X., McGowan, N., Pearson, N.J., Satsuawa, T., Shi, R., Williams, P., Xiong, Q., Yang, J.S., Zhang, M., O’Reilly, S.Y. (2016) Mantle Recycling: Transition Zone Metamorphism of Tibetan Ophiolitic Peridotites and its Tectonic Implications. Journal of Petrology 57, 655–684.
 Show in context
Show in context The discovery of nano- to micrometre scale grains of diamond separated from ophiolitic rocks has recently attracted the attention of geoscientists due to its potential evidence for lithosphere recycling down to, or below, the mantle Transition Zone (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
The debate, however, rejuvenated after findings of other UHP minerals such as coesite together with super-reduced phases in many chromitites and associated peridotites of ophiolites worldwide (e.g., Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019a) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
Grozeva, N.G., Klein, F., Seewald, J.S., Sylva, S.P. (2020) Chemical and isotopic analyses of hydrocarbon-bearing fluid inclusions in olivine-rich rocks. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 378, 20180431.
 Show in context
Show in context However, brucite is a widespread product in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions in ophiolitic samples (e.g., Klein et al., 2019; Grozeva et al., 2020).
View in article
Klein, F., Grozeva, N.G., Seewald, J.S. (2019) Abiotic methane synthesis and serpentinization in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 116, 17666–17672.
 Show in context
Show in context However, brucite is a widespread product in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions in ophiolitic samples (e.g., Klein et al., 2019; Grozeva et al., 2020).
View in article
Sub-surface fluid inclusions lack water and are dominated by methane (Table S-2), similarly to olivine-hosted fluid inclusions described by Klein et al. (2019).
View in article
Fluid infiltration in oceanic lithosphere is commonly associated with sporadic deformation events that trigger an increase of porosity by (micro-)fracturing during cooling below the brittle-ductile transition of olivine (Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
Comprehensive thermodynamic models of these processes in ultramafic and oceanic rocks (McCollom and Bach, 2009; Klein et al., 2019) show that below ∼350 °C (at <200 MPa) in the stability field of serpentine + brucite “serpentinisation” of the walls of olivine hosting fluid inclusions consumes H2O in the fluid and generates H2 through precipitation of Fe3+-rich phases, particularly magnetite, so that consumption of inorganic carbon (CO2) and formation of abiotic CH4 takes place. In the 6 component system MgO-FeO-SiO2-C-O2-H2, the formation of phase assemblages made of serpentine, brucite, magnetite, diamond and CH4-fluid from an initial assemblage made of olivine and H2O-CO2 fluid can be described by a number of linearly independent reactions.
View in article
Among many, the following set of five linearly independent reactions obtained with the software CSpace (Torres-Roldán et al., 2000) describes the process (commonly used as coupled reactions during serpentinisation, e.g., Lamadrid et al., 2017; Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
Admittedly, calculations in a more complex system, with additional components and minerals (e.g., CaO, clinopyroxene, talc, carbonates etc.) and constraints (e.g., dissolved silica in the fluid), and at other P-T conditions over which serpentinisation takes place, would yield a more intricate picture of the basic process outlined above and different absolute values of fO2 (e.g., Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
However, brucite is a widespread product in olivine-hosted fluid inclusions in ophiolitic samples (e.g., Klein et al., 2019; Grozeva et al., 2020).
View in article
However, a highly reduced environment (particularly at lower T, see e.g., Klein et al., 2019) should develop if CH4 is to be the main fluid species in the inclusions, making possible the metastable formation of nanodiamond in low pressure, olivine-bearing oceanic rocks during low T infiltration of H2O-CO2 fluid mixtures.
View in article
The undoubted natural origin of diamond hosted with serpentine, magnetite and CH4 in sealed fluid inclusions within magmatic olivine from a gabbro sill and associated chromitite should be related to the generalised release of CH4 during hydrothermal alteration (partial hydration) of shallow oceanic lithosphere (e.g., Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
Lamadrid, H.M., Rimstidt, J.D., Schwarzenbach, E.M., Klein, F., Ulrich, S., Dolocan, A., Bodnar, R.J. (2017) Effect of water activity on rates of serpentinization of olivine. Nature Communications 8, 1–9.
 Show in context
Show in context Among many, the following set of five linearly independent reactions obtained with the software CSpace (Torres-Roldán et al., 2000) describes the process (commonly used as coupled reactions during serpentinisation, e.g., Lamadrid et al., 2017; Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
Litasov, K.D., Kagi, H., Voropaev, S.A., Hirata, T., Ohfuji, H., Ishibashi, H., Makino, Y., Bekker, T.B., Sevastyanov, V.S., Afanasiev, V.P., Pokhilenko, N.P. (2019a) Comparison of enigmatic diamonds from the Tolbachik arc volcano (Kamchatka)and Tibetan ophiolites: Assessing the role of contamination by synthetic materials. Gondwana Research 75, 16–27.
 Show in context
Show in context In this regard, Litasov et al. (2019a,b) have recently claimed that most diamonds, if not all, from ophiolitic rocks are not natural but instead have a synthetic origin, and emphasised the need to identify diamond below the polished surface of the host mineral.
View in article
Litasov, K.D., Kagi, H., Bekker, T.B., Hirata, T., Makino, Y. (2019b) Cuboctahedral type Ib diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites and peridotites: the evidence for anthropogenic contamination. High Pressure Research 39, 480–488.
 Show in context
Show in context In this regard, Litasov et al. (2019a,b) have recently claimed that most diamonds, if not all, from ophiolitic rocks are not natural but instead have a synthetic origin, and emphasised the need to identify diamond below the polished surface of the host mineral.
View in article
Manuella, F.C. (2013) Can nanodiamonds grow in serpentinite-hosted hydrothermal systems? A theoretical modelling study. Mineralogical Magazine 77, 3163–3174.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond.
View in article
However, it has been demonstrated that nanodiamond can form at super-reducing conditions (e.g., Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018).
View in article
Massonne, H.J. (2019) Comment: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e476, doi: 10.1130/G46459C.1.
 Show in context
Show in context However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
Whereas in other samples the natural origin of diamond has not been firmly proved (Massonne, 2019), here we provide several lines of evidence for a natural origin.
View in article
Such an observation meets the basic requirements for in situ mineral grains, as suggested by Massonne (2019).
View in article
McCollom, T.M., Bach, W. (2009) Thermodynamic constraints on hydrogen generation during serpentinization of ultramafic rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 73, 856–875.
 Show in context
Show in context Comprehensive thermodynamic models of these processes in ultramafic and oceanic rocks (McCollom and Bach, 2009; Klein et al., 2019) show that below ∼350 °C (at <200 MPa) in the stability field of serpentine + brucite “serpentinisation” of the walls of olivine hosting fluid inclusions consumes H2O in the fluid and generates H2 through precipitation of Fe3+-rich phases, particularly magnetite, so that consumption of inorganic carbon (CO2) and formation of abiotic CH4 takes place.
View in article
Pujol-Solà, N., Proenza, J., Garcia-Casco, A., González-Jiménez, J., Andreazini, A., Melgarejo, J., Gervilla, F. (2018) An Alternative Scenario on the Origin of Ultra-High Pressure (UHP) and Super-Reduced (SuR) Minerals in Ophiolitic Chromitites: A Case Study from the Mercedita Deposit (Eastern Cuba). Minerals 8, 433, doi: 10.3390/min8100433.
 Show in context
Show in context In this study we report for the first time in situ diamond grains hosted below the polished surface of magmatic olivine from a low pressure gabbro sill of the upper mantle section of the Moa-Baracoa Ophiolitic Massif, eastern Cuba (Supplementary Information; Figs. S-1–S-4, Table S-1), where super-reduced phases formed during serpentinisation have been previously reported (Pujol-Solà et al., 2018).
View in article
The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019a) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
Sachan, H.K., Mukherjee, B.K., Bodnar, R.J. (2007) Preservation of methane generated during serpentinization of upper mantle rocks: Evidence from fluid inclusions in the Nidar ophiolite, Indus Suture Zone, Ladakh (India). Earth and Planetary Science Letters 257, 47–59.
 Show in context
Show in context Brucite was not identified in any of the studied inclusions, similar to other locations (e.g., Sachan et al., 2007).
View in article
Schmidt, M.W., Gao, C., Golubkova, A., Rohrbach, A., Connolly, J.A. (2014) Natural moissanite (SiC) – a low temperature mineral formed from highly fractionated ultra-reducing COH-fluids. Progress in Earth and Planetary Science 1, 27.
 Show in context
Show in context The corresponding calculated log(fO2; MPa) is as low as −45.3, (ΔlogfO2[Iron-Magnetite] = −6.5; Frost, 1991), consistent with thermodynamic calculations in the diamond-COH fluid system at 350 °C and 100 MPa (Fig. 3; cf. Schmidt et al., 2014).
View in article
Simakov, S.K. (2018) Nano- and micron-sized diamond genesis in nature: An overview. Geoscience Frontiers 9, 1849–1858.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond. However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
However, it has been demonstrated that nanodiamond can form at super-reducing conditions (e.g., Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018).
View in article
Simakov, S.K., Dubinchuk, V.T., Novikov, M.P., Drozdova, I.A. (2008) Formation of diamond and diamond-type phases from the carbon-bearing fluid at PT parameters corresponding to processes in the Earth’s crust. Doklady Earth Sciences 421, 835–837.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond. However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
Simakov, S.K., Kouchi, A., Mel’nik, N.N., Scribano, V., Kimura, Y., Hama, T., Suzuki, N., Saito, H., Yoshizawa, T. (2015) Nanodiamond finding in the hyblean shallow mantle xenoliths. Scientific Reports 5, 10765, doi: 10.1038/srep10765.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond. However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
Simakov, S.K., Scribano, V., Mel’Nik, N.N., Barone, G. (2020) Sicilian serpentinite xenoliths containing abiotic organics with nanodiamond clusters as key model for prebiotic processes. Geoscience Frontiers (in press), doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2020.04.008.
 Show in context
Show in context Recently, the finding of in situ diamond in chromite-hosted fluid inclusions from ophiolitic chromitites by Farré-de-Pablo et al., (2019a) provided the first evidence for empirical (Simakov et al., 2015, 2020), experimental (Simakov et al., 2008) and theoretical (Manuella, 2013; Simakov, 2018) work on low pressure growth of diamond. However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
Torres-Roldán, R.L., Garcia-Casco, A., García-Sánchez, P.A. (2000) CSpace: An integrated workplace for the graphical and algebraic analysis of phase assemblages on 32-bit Wintel platforms. Computers and Geosciences 26, 779–793.
 Show in context
Show in context Among many, the following set of five linearly independent reactions obtained with the software CSpace (Torres-Roldán et al., 2000) describes the process (commonly used as coupled reactions during serpentinisation, e.g., Lamadrid et al., 2017; Klein et al., 2019).
View in article
Whitney, D.L., Evans, B.W. (2010) Abbreviations for names of rock-forming minerals. American Mineralogist 95, 185–187.
 Show in context
Show in context Assuming 11 phase components (Fo, Fa, Mag, Mg-Srp, Mg-Brc, H2O, CO2, CH4, H2, SiO2(aq), C abbreviations after Whitney and Evans, 2010) appropriate for the low temperature stage of reaction progress, and excluding magnesite for simplicity, the dimension of the reaction space is 5.
View in article
Xiong, F., Liu, Z., Kapsiotis, A., Yang, J., Lenaz, D., Robinson, P.T. (2019) Petrogenesis of lherzolites from the Purang ophiolite, Yarlung-Zangbo suture zone, Tibet: origin and significance of ultra-high pressure and other ‘unusual’ minerals in the Neo-Tethyan lithospheric mantle. International Geology Review 61, 2184–2210.
 Show in context
Show in context Far-reaching geodynamic models have been proposed based on the assumption that diamond growth took place at UHP conditions in these rocks (e.g., Barron et al., 1996; Xiong et al., 2019 and references therein).
View in article
Yang, J.S., Dobrzhinetskaya, L., Bai, W.J., Fang, Q.S., Robinson, P.T., Zhang, J., Green, H.W. (2007) Diamond- and coesite-bearing chromitites from the Luobusa ophiolite, Tibet. Geology 35, 875–878.
 Show in context
Show in context The discovery of nano- to micrometre scale grains of diamond separated from ophiolitic rocks has recently attracted the attention of geoscientists due to its potential evidence for lithosphere recycling down to, or below, the mantle Transition Zone (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019a) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
Yang, J., Meng, F., Xu, X., Robinson, P.T., Dilek, Y., Makeyev, A.B., Wirth, R., Wiedenbeck, M., Cliff, J. (2015) Diamonds, native elements and metal alloys from chromitites of the Ray-Iz ophiolite of the Polar Urals. Gondwana Research 27, 459–485.
 Show in context
Show in context The discovery of nano- to micrometre scale grains of diamond separated from ophiolitic rocks has recently attracted the attention of geoscientists due to its potential evidence for lithosphere recycling down to, or below, the mantle Transition Zone (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
The presence of diamond (Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019a) and other highly reduced phases (e.g., metallic Si, moissanite; Pujol-Solà et al., 2018) in these rocks, in particular chromitites, cannot hence be taken as a general indication of ultra-high pressure conditions (e.g., Yang et al., 2007, 2015; Griffin et al., 2016).
View in article
Yang, J., Lian, D., Robinson, P.T., Qiu, T., Xiong, F., Wu, W. (2019) Comment to: A shallow origin for diamonds in ophiolitic chromitites. Geology 47, e475, doi: 10.1130/G46446C.1.
 Show in context
Show in context However, the debate on the natural origin of diamond continued (e.g., Farré-de-Pablo et al., 2019b; Massonne, 2019; Yang et al., 2019).
View in article
top
Supplementary Information
The Supplementary Information includes:
- Geological Setting and Petrography
- Methods
- Tables S-1 and S-2
- Figures S-1 to S-7
- Supplementary Information References
Download the Supplementary Information (PDF).
Figures
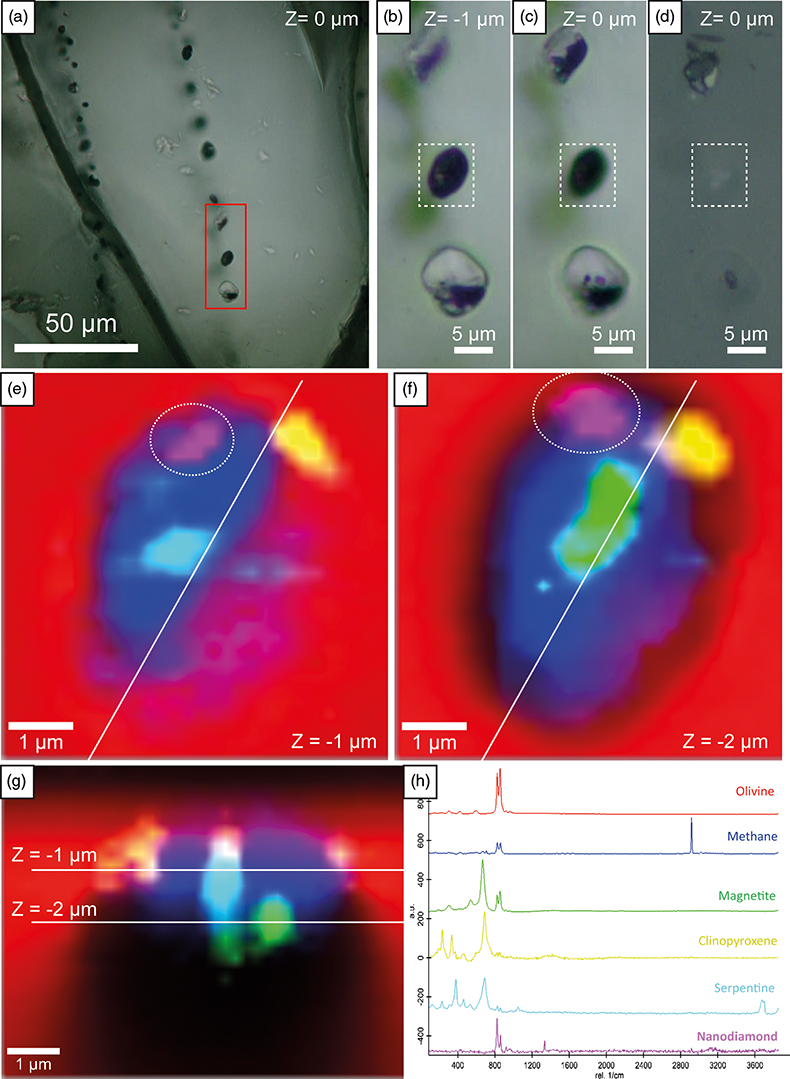
Figure 1 (a) Transmitted light photomicrograph (TLP) of olivine hosting a trail of secondary fluid inclusions. The red area defines the zoom in (b-d). (b, c) TLP of fluid inclusions below the surface of olivine with focus at Z (depth) = −1 and 0 μm respectively. (d) Reflected light photomicrograph of (c), showing that the central inclusion is completely below the surface. White rectangles mark the area of (e-g). (e) Fluid inclusion confocal Raman map at Z = −1 μm; different colours represent different phases. (f) Confocal Raman map for the same inclusion at Z = −2 μm. (g) Z-stack of (e, f) showing the inclusion profile. (h) Raman spectra of the identified phases (colour coded). Mapping conditions: 6 × 6 μm, 30 × 30 spectra, Tint = 2 s, 2 mW, 100× objective.
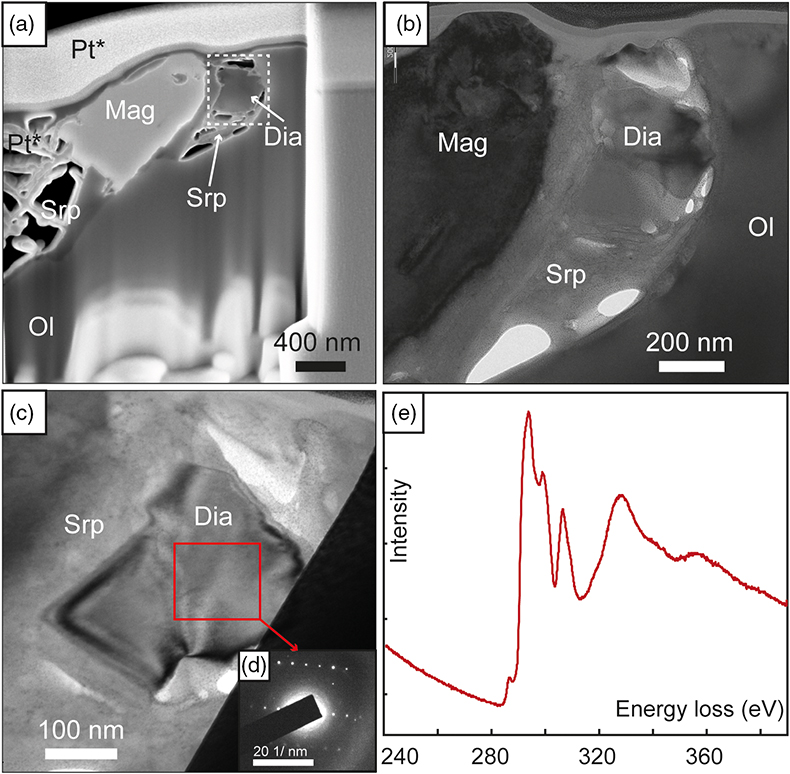
Figure 2 (a) Field emission scanning electron microscope image of olivine-hosted inclusion thinned by focused ion beam. (b,c) TEM image of the diamond and the surrounding serpentine and magnetite; the red square shows the selected area electron diffraction (SAED). (d) SAED pattern confirming the diamond structure of the crystal (the nearly horizontal rows of reflections have indices 111 with d spacing of 2 Å). (e) Electron energy loss near-edge structure of the C K-edge for the diamond showing a major peak due to its sp3 bonding. Abbreviations: Dia-Diamond, Mag-magnetite, Ol-olivine, Srp-serpentine, Pt*-platinum deposited during sample preparation.
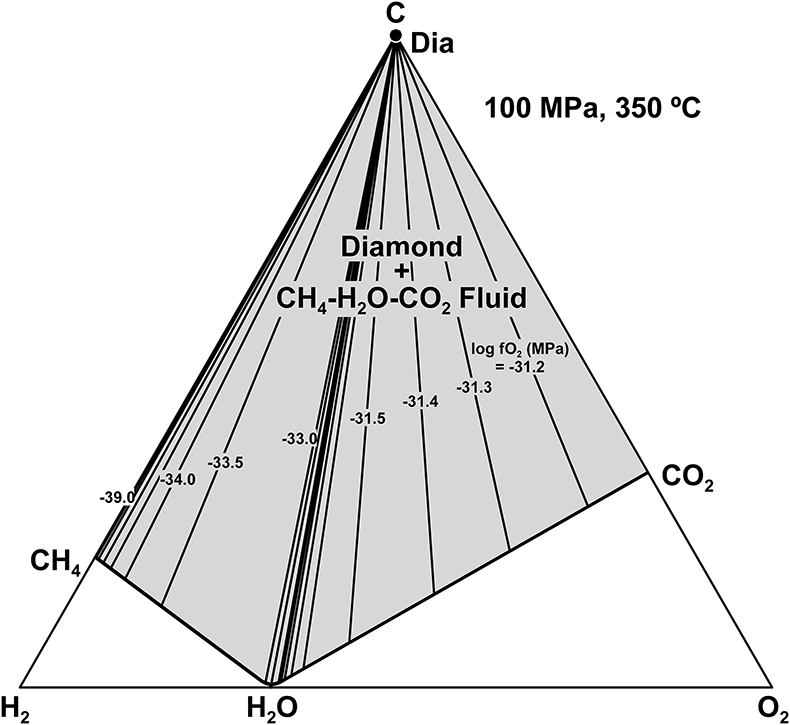
Figure 3 Phase relations in the C-O-H system (see methods in SI for details) with indication of fO2 isopleths (black solid lines, log-units) for the diamond-(Dia) saturated portion (log(aC) = 0) of the system at 100 MPa, 350 °C.